What is Intrahepatic Ectopic Pregnancy: Latest Case, Symptoms, Risks & Treatments
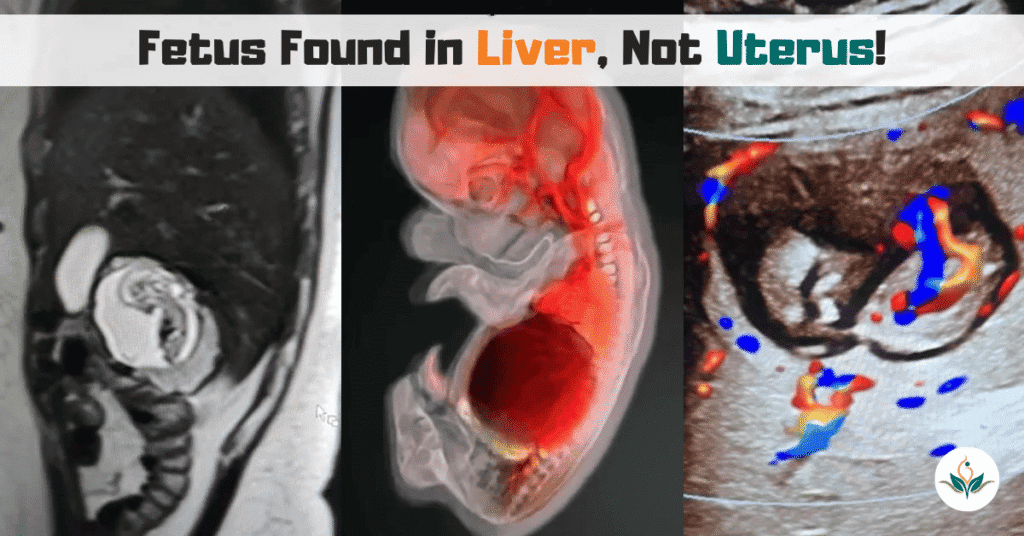
PCOD and PCOS: Causes, Symptoms, Differences and Treatment Published by Vishesh Hospital Facebook Instagram Youtube Intrahepatic ectopic pregnancy is one of the rarest forms of ectopic pregnancy, where a fertilized egg implants within the liver, rather than the uterus or fallopian tubes. Globally, fewer than eight cases have ever been documented, and its medical implications […]
PCOD and PCOS: Causes, Symptoms, Differences and Treatment

Dr. Nitya Agrawal | August 8, 2025 | Medical PCOD and PCOS: Causes, Symptoms, Differences and Treatment Published by Vishesh Hospital Facebook Twitter Youtube Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) are two of the most commonly discussed reproductive health conditions affecting women of reproductive age. Although their names are frequently used interchangeably, […]
What Is Menopause?

Vishesh Team July 13, 2025 Medical Navigating Menopause: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Natural Remedies, and Lifestyle Strategies for Women Published by Vishesh Hospital Facebook Twitter Youtube Welcome to our in-depth exploration of menopause, a natural phase in every woman’s life that marks the end of menstrual cycles and fertility. If you’re experiencing hot flashes, […]

