
Published by Vishesh Hospital
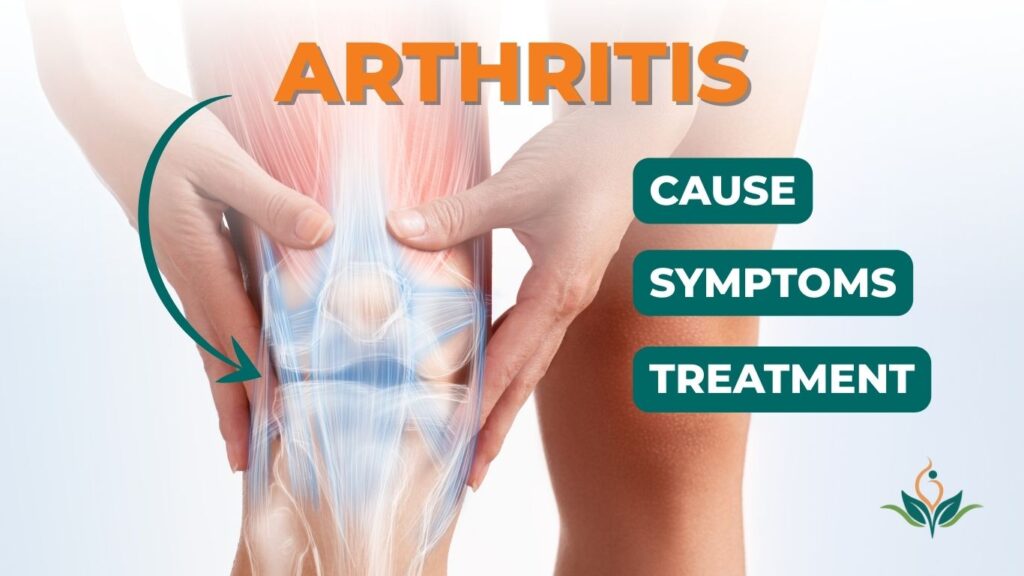
Arthritis is not a single disease but a complex group of over 100 related disorders that cause joint pain, swelling, and loss of mobility. Globally, arthritis is one of the most prevalent chronic health conditions, affecting both young and old, with a significant impact on daily living and quality of life. Staying informed about symptoms, types, and the latest breakthroughs is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
Arthritis manifests with a range of symptoms, which may vary in intensity and duration. The most common include:
Persistent joint pain and tenderness
Swelling or puffiness in affected joints
Stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity
Reduced range of motion and flexibility
Redness and warmth near the involved joint
Fatigue, low-grade fever (in some forms)
Difficulty performing regular tasks, such as climbing stairs or opening jars
Symptoms can develop suddenly or progress gradually and may affect one or multiple joints.
Arthritis has diverse causes:
Genetics: Family history raises susceptibility
Age: Risk increases with advancing age
Sex: Certain types (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis) are more common in women, while others (like gout) affect men more
Previous joint injury: Past damage can predispose joints to arthritis
Obesity: Excess weight puts additional strain on weight-bearing joints
Infection: Some forms of arthritis result from joint infections
Immune system dysfunction: The body mistakenly attacks its own joints (autoimmune arthritis)
Metabolic abnormalities: Gout, due to uric acid buildup, is a classic example.
| Type | Description & Key Features |
|---|---|
| Osteoarthritis | Wear-and-tear damage to joint cartilage; most common, especially in knees, hips, hands. |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | Immune system attacks the lining of joints; systemic, often affects both sides equally. |
| Psoriatic Arthritis | Associated with psoriasis; causes joint pain, swelling, and skin lesions. |
| Gout | Sudden, severe pain (often in the big toe); due to uric acid crystal accumulation. |
| Juvenile Arthritis | Affects children; joint pain, swelling, loss of motion. |
| Lupus | Autoimmune; can affect joints as well as organs like the kidneys and heart. |
| Ankylosing Spondylitis | Chronic inflammation mainly of the spine; can lead to fusion of vertebrae. |
Diagnosis involves:
Detailed medical history and physical examination
Blood tests (markers of inflammation, autoantibodies, uric acid, etc.)
Joint fluid analysis (for suspected gout or infection)
Imaging: X-rays, ultrasound, and MRI to assess the extent of joint damage.
Medication: Pain relievers (paracetamol), NSAIDs (ibuprofen, diclofenac), corticosteroids (short-term), and disease-modifying agents (DMARDs and biologics for inflammatory types).
Physical therapy: Tailored exercise programs to increase strength, mobility, and function.
Lifestyle: Weight management, balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, and smoking cessation.
Assistive devices: Braces, splints, walking aids.
Surgery: In advanced cases, options like joint replacement or arthroscopy.
Most forms cannot be cured, but many can be well controlled and even enter remission.
No—many people do well with medications, therapy, and lifestyle changes. Surgery is recommended only in advanced, disabling cases.
Yes. Ask about biologics, stem cell therapies, nerve stimulators, and recent clinical trial opportunities for advanced care.
Appointment
Don’t let gynecological issues impact your well-being. At Vishesh Hospital, our expert gynecology services in Nagpur provide compassionate care for every stage of a woman’s life. Whether you’re facing menstrual irregularities, planning a pregnancy, or need advanced treatment, our experienced team is here to support your health with confidence and care.





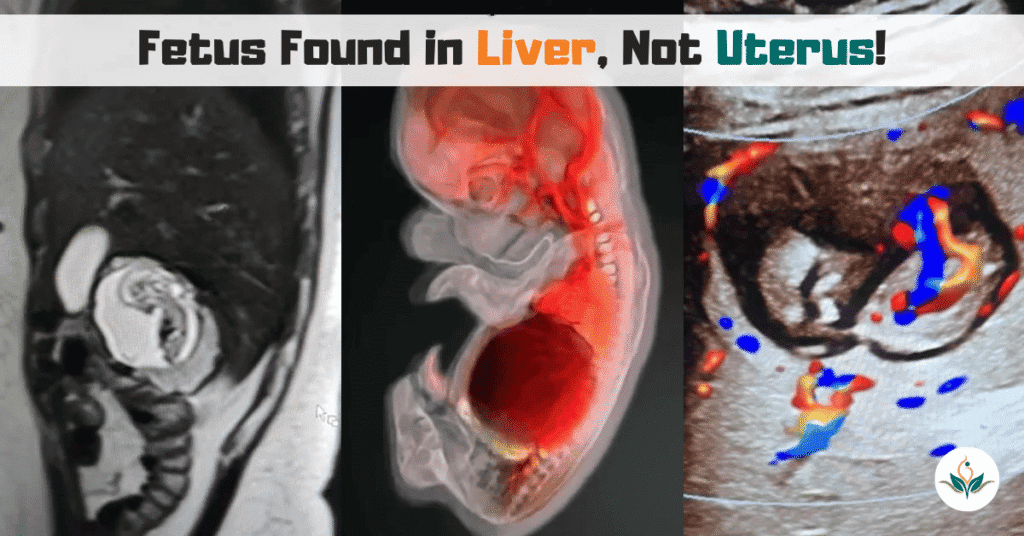



At Vishesh Hospital, we care with compassion, treat with dedication, and put every life first — because caring is at the heart of healing.
Copyright © 2025 Vishesh Hospital – Developed by Snyptech